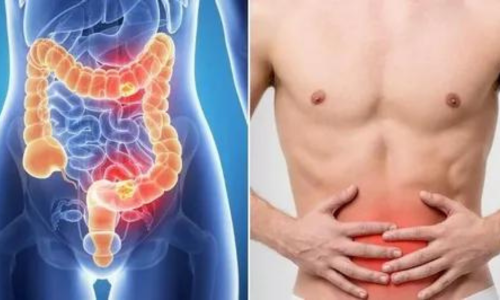
Colon cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the large intestine (colon). The colon is the final part of the digestive tract.
Colon cancer most commonly affects older adults, although it can appear at any age. It usually begins as small, noncancerous (benign) clumps of cells called polyps that form inside the colon. Over time, some of these polyps may become colon cancers.
Polyps may be small and produce few, if any, symptoms. For this reason, doctors recommend regular screenings to help prevent colon cancer by identifying and removing polyps before they turn into cancer.
In the case of colon cancer, there are many treatments available to help control it, including surgery, radiation therapy and drug therapies, such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Colon cancer is sometimes called colorectal cancer, which is a combination of colon cancer and rectal cancer, and it begins in the rectum.
Symptoms:

Signs and symptoms of colon cancer include:
A persistent change in bowel movement, whether diarrhea or constipation, or a change in the consistency of stool
•Anal bleeding, or blood in the stool
•Persistent abdominal disturbances, such as painful cramps, gas, or pain
•A feeling that the intestines are not completely empty
•Weakness or exhaustion
•Unexplained weight loss
Many people with colon cancer have no symptoms in the early stages of the disease. If symptoms do appear, they are likely to vary according to the size of the cancer and its location within the large intestine.
When do you visit the doctor?
If you notice any persistent symptoms that worry you, see your doctor.
Leave a Reply